The environmental impact of hipping a vehicle by sea is both positive and negative environmental impacts. While shipping is generally considered to be more environmentally friendly than air, rail or road transport, there are still environmental impacts that need to be considered when shipping a vehicle by sea.
Emission of Greenhouse Gases
One of the main environmental impacts of shipping a vehicle by sea is the emission of greenhouse gases.
Shipping is responsible for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions, with the majority of these emissions coming from the burning of fossil fuels by ships. These emissions contribute to climate change and can have negative impacts on the environment and public health.
To reduce the greenhouse gas emissions associated with shipping a vehicle by sea, it is important to choose a shipping company that uses fuel-efficient vessels and practices energy-efficient operations. It is also important to consider the carbon footprint of the entire shipping process, including the pickup and delivery of the vehicle, and to choose a shipping company that has a strong environmental record.
Accidents and Spills
As with any form of shipping, there is the potential for accidents and spills. When it comes to shipping vehicles by sea, this is compounded because the vehicles themselves pose an increased risk.
While shipping accidents are relatively rare, they can have serious consequences for the environment and wildlife. For example, oil spills from ships can have a devastating impact on marine ecosystems and wildlife, and can be difficult and costly to clean up.
To reduce the risk of accidents and spills with shipping, it is important to choose a reputable and experienced shipping company with a strong safety record. It is also important to follow all safety regulations and guidelines, and to ensure that the vehicle is properly secured and prepared for transport.
This is why we’re meticulous with regards to the shipping companies we partner with as well as vehicle preparation prior to shipping.
Positive Environmental Impact of Shipping a Vehicle by Sea
Shipping and transporting of goods is a part of society. Whether the need is global or national, there is a constant requirement for goods to be moved from one place to another.
The choice is no longer whether an item is to be transported but rather, how it will be transported.
There are several positive environmental impacts of shipping a vehicle by sea.
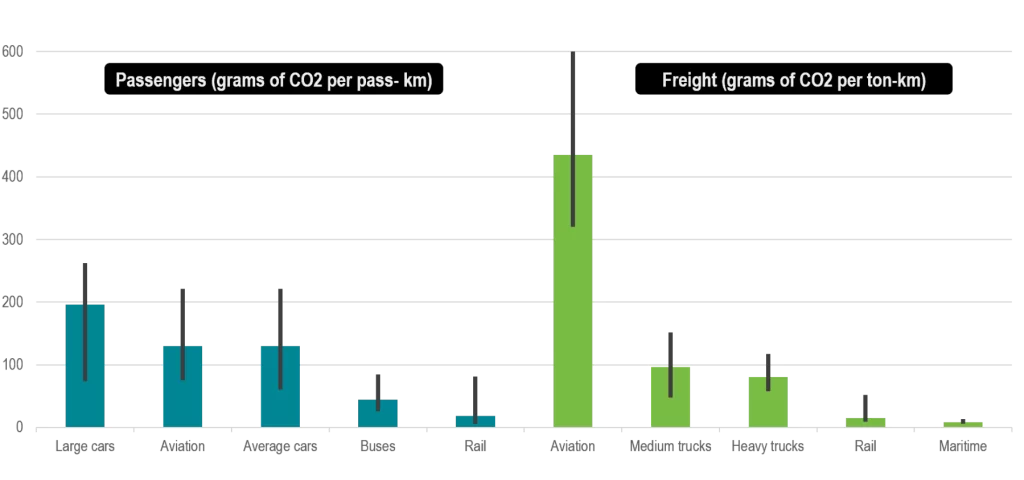
One of the main positive impacts is that shipping is generally more energy-efficient and produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions than other modes of transport. According to the International Maritime Organization, shipping is the most energy-efficient form of transport, with emissions per tonne-mile being significantly lower than those of air, road and rail transport.
Another positive impact of shipping a vehicle by sea is that it can help to reduce congestion and pollution on roads and highways.
Shipping a vehicle by sea can be a convenient and cost-effective alternative to driving, particularly for long distances or over challenging terrain. By reducing the number of vehicles on the road, shipping a vehicle by sea can help to reduce congestion, noise, and air pollution.
Vehicle shipping by sea can also help to reduce the need for new roads and infrastructure, which can have a positive impact on the environment.
Building new roads and infrastructure can have negative impacts on ecosystems and wildlife, and can contribute to the loss of natural habitat. By using existing shipping routes and infrastructure, it is possible to reduce the need for new construction and the associated environmental impacts.
Overall, shipping a vehicle by sea has several positive environmental impacts, including being more energy-efficient and producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions, reducing congestion and pollution on roads, and reducing the need for new infrastructure.